From dynasty to republic
(China Daily)
Updated: 2008-04-09 07:25
Updated: 2008-04-09 07:25
Tibet is located in Southwest China. The people who lived there struck up links with the Han in the Central Plains long before the Christian era. Throughout centuries, the numerous tribes scattered across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau gradually developed into the Tibetan ethnic group.

By the Tang Dynasty (AD 618-907), the Tibetans and Hans had, through marriages between royal families and other alliances, cemented unity and political friendship and formed close economic and cultural relations. This created a solid foundation for the ultimate founding of a unified nation.
A statue of the Tang Princess Wencheng, who married the Songtsan Gambo, the Tubo king, in 641, is still enshrined and worshiped at the Potala Palace in Lhasa, capital of the Tibet autonomous region.
The Tang-Tubo Alliance Monument, which marks the meeting between Tang and Tubo and was erected in 823, still stands in the square in front of the Jokhang Monastery. The monument's inscription reads in part: "The two kings, like uncle and nephew, having come to the agreement that their territories be united as one, have signed this alliance of great peace to last for eternity! May God and humanity bear witness thereto so that it may be praised from generation to generation."
In the mid-13th century, Tibet was officially incorporated into the territory of China's Yuan Dynasty. Since then, although China experienced several dynastic changes, Tibet has remained under the jurisdiction of the central government of China.
|
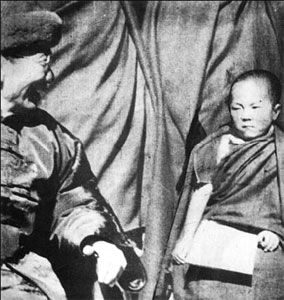
Wu Zhongxin, chief of the Commission for Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs of the Republic of China, and the current Dalai Lama before his installation ceremony in 1940. File photo |
Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368)
The Yuan emperor established the Xuanzhengyuan, or Ministry for the Spread of Governance, to directly handle important military and political affairs involving the Tibet region. The emperor selected the people working for the ministry, and its reports were submitted directly to the monarch.
The central government of the Yuan Dynasty sent officials into Tibet to set up post stations, which varied in size according to the local population, topography and resources. These stations were linked up in a communication line extending from Tibet up to Dadu (present-day Beijing).
Ming Dynasty (1368-1644)
In 1368, the Ming Dynasty replaced the Yuan Dynasty in China and inherited the right to rule Tibet.
The central government of the Ming Dynasty retained most of the titles and ranks of official positions instituted during the Yuan Dynasty. The Dbus-Gtsang Itinerant High Command was set up in the central part of present-day Tibet, while the Mdo-khams Itinerant High Command covered the eastern part. Equivalent to provincial-level military organs, they operated under the Shaanxi Itinerant High Command and, at the same time, handled civil administration. In Ngari in west Tibet, the E-Li-Si Army-Civilian Marshal Office was instituted. Leading officials of these organs were all appointed by the central government.
Any official of the Tibetan local government who offended the law was punished by the central government.
The Dalai Lama and the Bainqen Lama are the two leading incarnation hierarchies of the Gelug Sect of Tibetan Buddhism. The Gelug Sect rose during the Ming Dynasty, and the third Dalai Lama was the abbot of one of the sect's monasteries. The central government of the Ming Dynasty showed him special favor by allowing him to pay tribute. In 1587, he was granted the title of Dorjichang or Vajradhara Dalai Lama.
Qing Dynasty (1644-1911)
When the Qing Dynasty replaced the Ming Dynasty in 1644, it strengthened administration of Tibet. In 1653, the Qing emperor granted an honorific title to the fifth Dalai Lama and then did the same for the fifth Bainqen Lama in 1713, officially establishing the titles of the Dalai Lama and the Bainqen Erdeni, and their political and religious status in Tibet.
The Dalai Lama ruled the bulk of the territory from Lhasa, while the Bainqen Erdeni ruled the rest of Tibet from Xigaze.
In 1719, Qing government troops were sent into Tibet to dispel the Zungar forces, which had been entrenched in Lhasa for three years, and set out to reform Tibet's administrative system. The Qing emperor made a young Living Buddha from the Xikang area the seventh Dalai Lama and had him escorted into Tibet. He designated four Tibetan officials renowned for meritorious service as "Galoins" to handle Tibet's political affairs.
From 1727, high commissioners were stationed in Tibet to supervise local administration on behalf of the central authorities. Officials were also assigned about this time to survey and delimit the borders between Tibet (known in Chinese as Xizang) and Sichuan, Yunnan and Qinghai. The Qing government held the power to confirm the reincarnation of all deceased Living Buddhas of Tibet, including the Dalai Lama and the Bainqen Erdeni.
When the reincarnate boy was found, his name would be written on a lot, which would be put into a gold urn bestowed by the central government.
The high commissioners would bring together appropriate high-ranking Living Buddhas to determine the authenticity of the reincarnate boy by drawing lots from the gold urn. (Both the gold urn and lots are still preserved in Lhasa.)
The tonsure of the incarnate Living Buddha, his religious name, the choice of the master to initiate him into the monkhood and his sutra instructor all had to be announced by the high commissioners to the imperial court for examination and approval. The central government would send high officials to supervise the installation ceremony for the new Dalai Lama and the new Bainqen Erdeni and also the ceremony for their taking up the reins of government when they came of age.
Republic of China (1912-49)
In the autumn of 1911, revolution took place in China's interior, overthrowing the 270-year-old rule of the Qing Dynasty and establishing the Republic of China.
|
The 14th Dalai Lama (front) and the 10th Bainqen Erdeni cast their ballots for the drafting of the constitution during the first session of the first National People's Congress in 1954 in Beijing. File photo |
Upon its founding, the Republic of China declared itself a unified republic of the Han, Manchu, Mongol, Hui, Tibetan and other ethnic groups. In his inauguration statement on January 1, 1912, Sun Yat-sen, the provisional first president of the Republic of China, declared to the world: "The foundation of the country lies in the people, and the unification of lands inhabited by the Han, Manchu, Mongol, Hui and Tibetan people into one country means the unification of the Han, Manchu, Mongol, Hui and Tibetan into one people. It is called national unification."
In March, the Nanjing-based provisional senate of the Republic of China promulgated the republic's first constitution, the Provisional Constitution of the Republic of China, in which it was clearly stipulated that Tibet was a part of the territory of the Republic of China.
When the Chinese Kuomintang formed the national government in 1927 in Nanjing and held the national assembly in 1931, both the 13th Dalai Lama and the ninth Bainqen Erdeni sent representatives.
After the Nanjing national government was set up, a Commission for Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs was established in 1929 to handle the administrative affairs of the Tibetans, Mongolians and other ethnic minorities.
Despite the fact that incessant foreign aggression and civil wars weakened the central government of the Republic of China, it continued to grant honorific titles to the Dalai Lama and the Bainqen Erdeni. On many occasions the Dalai Lama and the Bainqen Erdeni expressed their support for national unification and for the central government.
The death of the 13th Dalai Lama in December 1933 was reported to the central government by the Tibetan local government in the traditional manner. The national government sent a special envoy to Tibet for the memorial ceremony.

The local Tibetan government also followed the age-old system in reporting to the central government all the procedures that should be followed in the search for the reincarnation of the late 13th Dalai Lama.
The present 14th Dalai Lama was born in Qinghai province. Originally named Lhamo Toinzhub, he was selected as one of the incarnate boys at age 2. After receiving a report submitted by the local Tibetan government in 1939, the central government ordered the Qinghai authorities to send troops to escort him to Lhasa.
After an inspection tour in Lhasa by Wu Zhongxin, chief of the Commission for Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs, in 1940, Chiang Kai-shek, then head of the central government, approved Tibetan Regent Razheng's request to waive the lot-drawing convention, and the chairman of the national government issued an official decree conferring the title of the 14th Dalai Lama on Lhamo Toinzhub.
People's Republic of China
The People's Republic of China was founded in 1949. In January 1950, the central government formally notified the local authorities of Tibet to "send delegates to Beijing to negotiate the peaceful liberation of Tibet".
The central government's adherence to the policy of peaceful negotiations greatly supported and inspired the patriotic forces in Tibet.
On May 23, 1951, the Agreement of the Central People's Government and the Local Government of Tibet on Measures for the Peaceful Liberation of Tibet (also known as the 17-Article Agreement) was signed after the delegates of the central people's government and the Tibetan local government agreed on a series of questions concerning Tibet's peaceful liberation.
A conference of all ecclesiastic and secular officials and representatives of the three most prominent monasteries was called by the local Tibetan government between Sept 26 and 29, 1951, to discuss the agreement. A report to the Dalai Lama was approved at the end of the conference.
It stated: "The 17-Article Agreement that has been signed is of great and unrivaled benefit to the grand cause of the Dalai and to Buddhism, politics, economy and other aspects of life in Tibet.
"Naturally, it should be implemented."
Xinhua

(China Daily 04/09/2008 page5)
|
||
|
||
|
|
|
|